Add a stylesheet
Overview
Cascading stylesheets are an important part of any frontend user interface. The default starter is configured to import a main.css file that you can edit, but you may prefer to import your stylesheet into a JavaScript file, or to use an alternate format such as Syntactically Awesome Style Sheets, aka SCSS. This guide illustrates how to configure webpack to import a stylesheet by walking through building a contact dapp. If you already know how to add cascading stylesheets (CSS) to a webpack-based project, you can skip this guide.
This guide illustrates using the React framework to manage the Document Object Model (DOM) for your frontend. Because React has its own custom DOM syntax, you need to modify the webpack configuration to compile the frontend code, which is written in JSX. For more information about learning to use React and JSX, see getting started on the React website.
Prerequisites
Before starting the guide, verify the following:
You have
node.jsinstalled for frontend development and can install packages usingnpm installin your project. For information about installing node for your local operating system and package manager, see the Node website.You have downloaded and installed the IC SDK package as described in the download and install page.
This guide requires you to use the IC SDK version 0.8.0 or later.
You have installed the Visual Studio Code plugin for Motoko as described in VS Code extensions for ICP development if you are using Visual Studio Code as your IDE.
You have started
dfxwith the commanddfx start --clean --background.
Create a new project
To create a new project directory for your custom frontend dapp:
Step 1: Open a terminal shell on your local computer, if you don’t already have one open.
Step 2: Change to the folder you are using for your Internet Computer projects, if you are using one.
Step 3: Verify that you have
node.jsinstalled locally, if necessary.Step 4: Create a new project by running the following command:
- dfx v0.17.0 or newer
- dfx v0.16.1 or older
Use dfx new <project_name> to create a new project:
dfx new contacts
You will be prompted to select the language that your backend canister will use:
? Select a backend language: ›
❯ Motoko
Rust
TypeScript (Azle)
Python (Kybra)
Then, select a frontend framework for your frontend canister. Select 'React':
? Select a frontend framework: ›
SvelteKit
❯ React
Vue
Vanilla JS
No JS template
No frontend canister
Lastly, you can include extra features to be added to your project:
? Add extra features (space to select, enter to confirm) ›
⬚ Internet Identity
⬚ Bitcoin (Regtest)
⬚ Frontend tests
dfx new contacts
Step 5: Change to your project directory by running the following command:
cd contacts
If you’ve never used React before, you might want to explore the intro to React tutorial or the React website before editing the frontend code.
Modify the default program
For this guide, you are going to modify the main program to with code that allows you to store and look up contact information.
To modify the default program:
Step 1: Open the
src/contacts_backend/main.mofile in a text editor and delete the existing content.Step 2: Copy and paste this code into the file:
import List "mo:base/List";
import AssocList "mo:base/AssocList";
actor Contact {
var contacts : ContactsMap = List.nil();
type Name = Text;
type Phone = Nat;
type Entry = {
name : Name;
address1 : Text;
address2 : Text;
email : Text;
phone : Phone;
};
type ContactsMap = AssocList.AssocList<Name, Entry>;
func nameEq(lhs : Name, rhs : Name) : Bool {
return lhs == rhs;
};
public func insert(name : Name, address1 : Text, address2 : Text, email : Text, phone : Phone) : async () {
let newEntry : Entry = {
name;
address1;
address2;
email;
phone;
};
let (newContacts, _) = AssocList.replace(
contacts,
name,
func(n: Name, m: Name) : Bool { n == m },
?newEntry
);
contacts := newContacts;
};
public query func lookup(name : Name) : async ?Entry {
return AssocList.find(contacts, name, nameEq);
};
};
Step 3: Save your changes and close the
main.mofile to continue.
Modify the frontend files
You are now ready to create a new frontend for your program.
Step 1: Open the webpack configuration file (
webpack.config.js) in a text editor.Step 2: Modify the frontend entry to replace the default index.html with index.jsx.
entry: {
// The frontend.entrypoint points to the HTML file for this build, so you need
// to replace the extension to `.js`.
index: path.join(__dirname, frontend_entry).replace(/\.html$/, ".jsx"),
},
Step 3: Locate the commented example for the
modulekey above thepluginssection, then uncomment the following lines:
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.(js|ts)x?$/, loader: "ts-loader" },
{ test: /\.css$/, use: ['style-loader','css-loader'] }
]
},
These settings enable your program to use the ts-loader compiler and to import CSS files.
Note: if you want to add support for `.scss` or `.sass` files, you should install `sass-loader` with:
npm install --save react react-dom
and then add this additional rule beneath the css-loader rule in webpack.config.js:
module: {
rules: [
// ...
{
test: /\.s[ac]ss$/i,
use: [
// Creates `style` nodes from JS strings
"style-loader",
// Translates CSS into CommonJS
"css-loader",
// Compiles Sass to CSS
"sass-loader",
],
},
]
},
Step 4: Save your changes and close the
webpack.config.jsfile to continue.Step 5: Create a new file named
tsconfig.jsonin the root directory for your project.Step 6: Open the
tsconfig.jsonfile in a text editor, then copy and paste this code into the file:
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "es2018", /* Specify ECMAScript target version: 'ES3' (default), 'ES5', 'ES2015', 'ES2016', 'ES2017', 'ES2018', 'ES2019' or 'ESNEXT'. */
"lib": ["ES2018", "DOM"], /* Specify library files to be included in the compilation. */
"allowJs": true, /* Allow javascript files to be compiled. */
"jsx": "react", /* Specify JSX code generation: 'preserve', 'react-native', or 'react'. */
},
"include": ["src/**/*"],
}
Step 7: Save your changes and close the
tsconfig.jsonfile to continue.
Add a stylesheet to your project
You are now ready to create a new cascading stylesheet and add it to your project.
To add a stylesheet:
Step 1: Change to the
src/contacts_frontend/assetsdirectory.cd src/contacts_frontend/assets/Step 2: Open the
main.cssfile in a text editor and delete the existing content.Step 3: Define some style properties for the frontend.
Replace the existing code with the following:
html {
background-color: bisque;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
display: block;
margin: 10px;
}
h1 {
color: darkblue;
font-size: 32px;
}
div.new-entry {
margin: 30px 20px 30px 20px;
}
.new-entry > div {
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
table {
margin-top: 12px;
border-top: 1px solid darkblue;
border-bottom: 1px solid darkblue;
}
#form {
margin: 30px 0 30px 20px;
}
button {
line-height: 20px;
}
#lookupName {
margin-right: 12px;
}
Step 4: Save your changes and close the
main.cssfile to continue.Step 5: Change to the
src/contacts_frontend/srcdirectory.Step 6: Open the default
index.jsfile in a text editor and delete the existing content.Step 7: Copy and paste this code into the
index.jsfile:
import * as React from "react";
import { render } from "react-dom";
import { contacts } from "../../declarations/contacts_backend";
import "../assets/main.css";
const Contact = () => {
async function doInsert() {
let name = document.getElementById("newEntryName").value;
let add1 = document.getElementById("newEntryAddress1").value;
let add2 = document.getElementById("newEntryAddress2").value;
let email = document.getElementById("newEntryEmail").value;
let phone = document.getElementById("newEntryPhone").value;
contacts_backend.insert(name, add1, add2, email, parseInt(phone, 10));
}
async function lookup() {
let name = document.getElementById("lookupName").value;
contacts_backend.lookup(name).then((opt_entry) => {
let entry;
if (opt_entry.length == 0) {
entry = { name: "", description: "", phone: "" };
} else {
entry = opt_entry[0];
}
document.getElementById("newEntryName").value = entry.name;
document.getElementById("newEntryAddress1").value = entry.address1;
document.getElementById("newEntryAddress2").value = entry.address2;
document.getElementById("newEntryEmail").value = entry.email;
document.getElementById("newEntryPhone").value = entry.phone.toString();
});
}
return (
<div className="new-entry">
<h1>My Contacts</h1>
<div>
Add or update contact information:
<form id="contact">
<table>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Name:</td>
<td>
<input id="newEntryName"></input>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Address 1 (street):</td>
<td>
<input id="newEntryAddress1"></input>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Address 2 (city and state):</td>
<td>
<input id="newEntryAddress2"></input>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Email:</td>
<td>
<input id="newEntryEmail"></input>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Phone:</td>
<td>
<input id="newEntryPhone" type="number"></input>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</form>
</div>
<div>
<button onClick={() => doInsert()}>Add Contact</button>
</div>
<div>
Lookup name:{" "}
<input id="lookupName" style={{ lineHeight: "20px" }}></input>
<button onClick={() => lookup()}>Lookup</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
document.title = "DFINITY CONTACT EXAMPLE";
render(<Contact />, document.getElementById("contacts"));
Step 8: Rename the modified
index.jsfile asindex.jsxby running the following command:
mv index.js index.jsx
Step 9: Open the default
src/contacts_assets/src/index.htmlfile in a text editor, then remove themain.csslink and update thebodycontents with<div id="contacts"></div>.For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>contacts</title>
<base href="/" />
</head>
<body>
<main>
<div id="contacts"></div>
</main>
</body>
</html>
Step 10: Navigate back to the root of your project directory.
Start the local network
Before you can build the contacts project, you need to connect to the local canister execution environment.
To start the environment locally:
Step 1: Open a new terminal window or tab on your local computer.
Step 2: Start the local canister execution environment on your local computer by running the following command:
dfx start --clean --background
After the environment completes its startup operations, you can continue to the next step.
Register, build, and deploy the dapp
After you connect to the local canister execution environment in your development environment, you can register, build, and deploy your dapp for testing.
To deploy the dapp:
Step 1: Check that you are still in the root directory for your project, if needed.
Step 2: Register, build, and deploy your dapp by running the following command:
dfx deploy
The dfx deploy command output displays information about the operations it performs.
Keep in mind that because you are running the canister execution environment locally, the identifiers displayed when you run the dfx deploy command are only valid on your machine.
To deploy canisters on ICP, you must specify that you are deploying to the Internet Computer and not your local environment by using the --network command-line option:
dfx deploy --network=ic
Step 3: Start the Webpack development server:
npm start
View the frontend
You can now access the frontend for the contacts dapp.
To view the frontend:
Step 1: Open a browser and navigate to the
http://localhost:4943.Step 2: Verify that you are prompted with a "My Contacts" form.
For example:
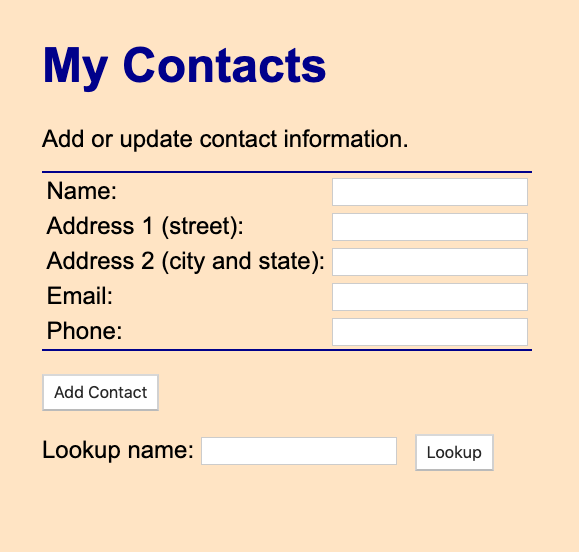
Step 3: Create one or more test records by entering text in the Name, Address, and Email input fields and a number in the Phone input field, then clicking Add Contact.
Step 4: Clear the form fields and type a contact name in the Lookup name field, then click Lookup to see the stored contact information.
Keep in mind that the Lookup name you type must be an exact match for the name of a contact you added.
Modify the stylesheet and test your changes
After viewing the Contacts dapp, you might want to make some changes.
To change stylesheet properties:
Step 1: Open the
src/contacts_assets/assets/mycontacts.cssfile in a text editor and modify its style settings.For example, you might want to change the background color or style the input form.
You should see the changes update immediately in your open browser window.
Modify the frontend or backend code
If you want to explore further, you might want to experiment with modifying the frontend or backend code for this guide. For example, you might want try modifying the guide to do the following:
Change the frontend code to clear the input fields after adding a new contact, for example, as part of an
onClickevent.Change the Motoko program functions to do partial instead of exact string matching on the
Namefield. (You will need to rundfx deployto test your changes on the local environment).Change the Motoko program to allow lookups based on a different field.
Stop the local canister execution environment
After you finish experimenting with your program, you can stop the local environment so that it doesn’t continue running in the background.
To stop the local development environment:
Step 1: In the terminal that displays your webpack dev server, press Control-C to interrupt the development server.
Step 2: Stop the Internet Computer network by running the following command:
dfx stop